As technology continues to advance, automated welding processes are becoming more prevalent in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Among these processes, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), commonly known as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, is highly regarded for its precision and quality. However, like any welding process, automated GTAW welding also presents its own set of challenges. In this blog, we will explore some of the common challenges associated with automated GTAW welding and discuss potential solutions to overcome them.
Challenge 1: Precise Control of Welding Parameters
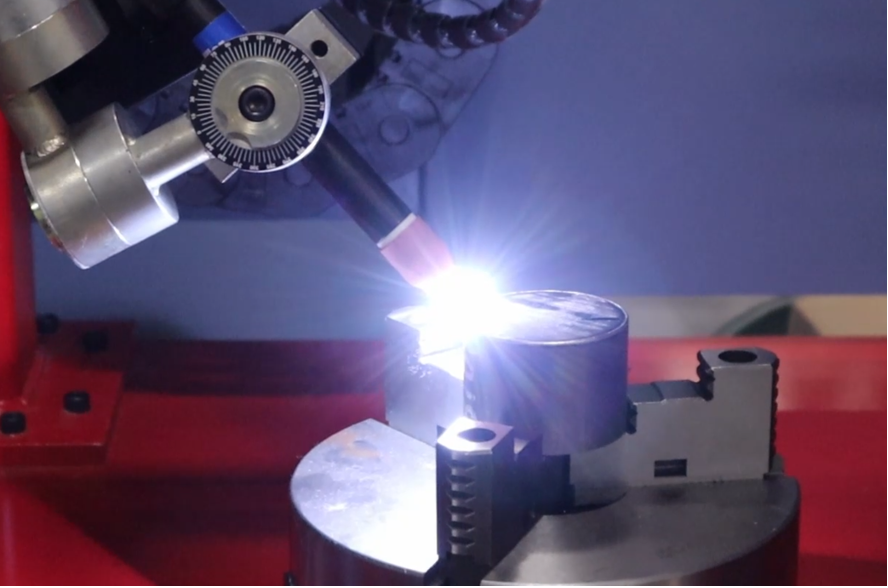
One of the critical aspects of automated GTAW welding is maintaining precise control over welding parameters, such as arc length, voltage, amperage, travel speed, WFS, and heat input. Any deviation from the optimal parameters can result in weld defects, such as lack of fusion, porosity, or incomplete penetration. Achieving consistent and precise control over welding parameters can be challenging due to factors such as material variations, joint fit-up, and changing welding positions.
Solution: Advanced Welding Automation Technology
To overcome this challenge, investing in advanced welding automation technology is crucial. Modern automated welding systems often come equipped with advanced features such as closed-loop control, real-time monitoring, and adaptive welding techniques. These technologies allow for precise control and monitoring of welding parameters throughout the welding process, ensuring consistent and high-quality welds. Additionally, using sensors, cameras, and feedback systems can provide real-time data, enabling adjustments to be made in real-time, resulting in improved welding accuracy and efficiency.
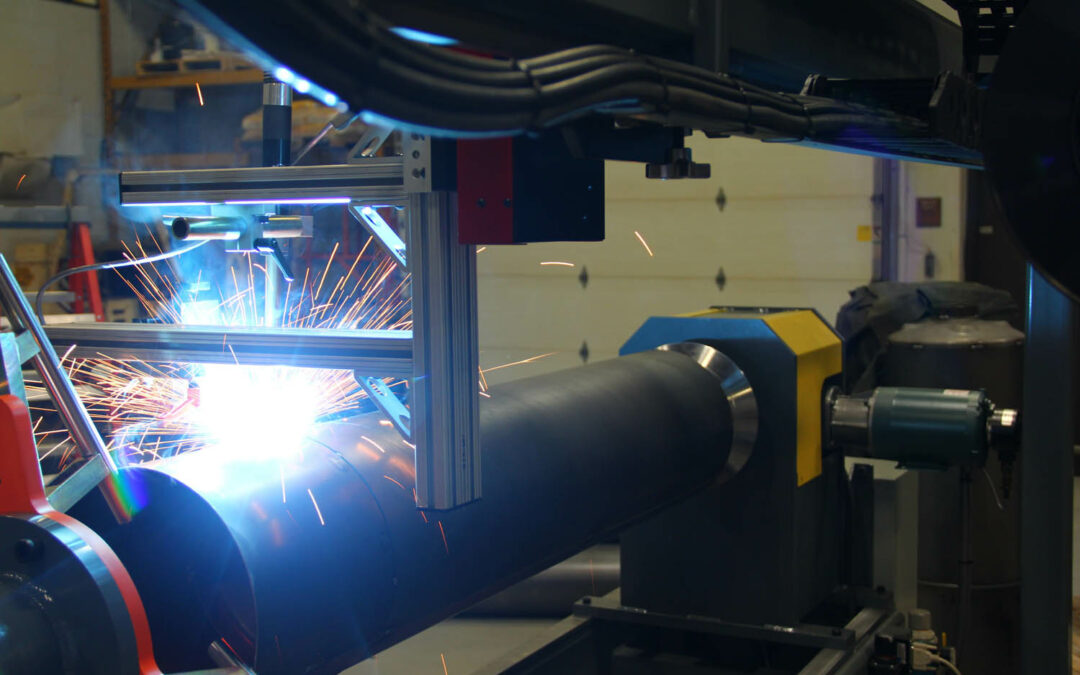
Challenge 2: Joint Fit-Up and Alignment
Achieving proper joint fit-up and alignment is crucial for successful GTAW welding. In automated welding, the joint fit-up and alignment can vary due to factors such as tolerances in parts, variations in material thickness, and fixture inaccuracies. Poor joint fit-up and alignment can lead to uneven heat distribution, lack of fusion, and distortion in the final weld.
Solution: Precise Fixturing and Sensing Technologies
To address this challenge, precise fixturing and sensing technologies can be employed. Fixtures and clamps can be designed to hold the workpieces securely in place, ensuring proper alignment during welding. Sensing technologies, such as laser sensors or vision systems, can be integrated into the automated welding system to monitor joint fit-up and alignment in real-time. These technologies provide feedback to the system, allowing for adjustments to be made to ensure accurate joint fit-up and alignment, resulting in high-quality welds.
Weld seam tracking system
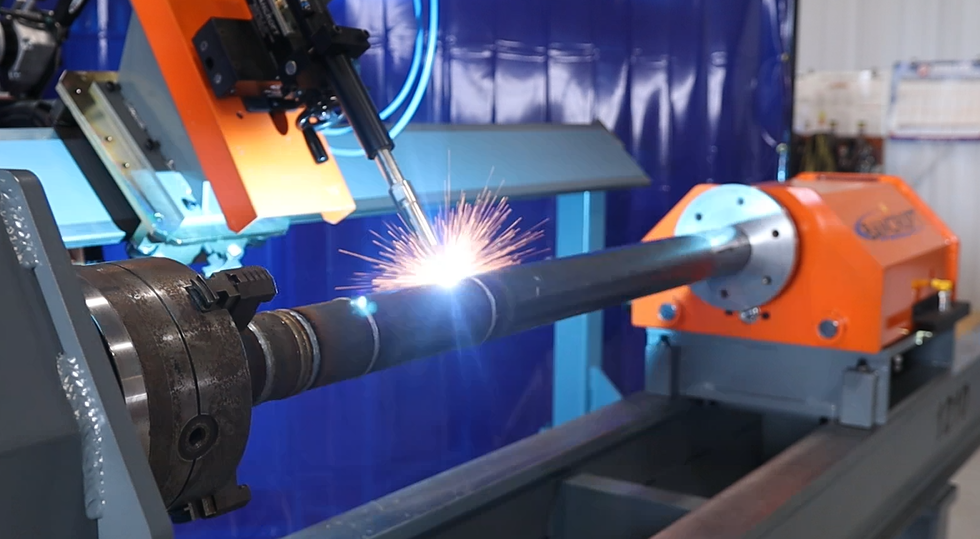
Challenge 3: Welding of Complex Geometries
In some applications, automated GTAW welding may be required for welding complex geometries, such as curved or contoured parts. Welding on curved surfaces can present challenges such as maintaining consistent arc length, achieving proper penetration, and avoiding weld defects due to changes in joint angles.
Solution: Robotic Welding Systems with Multi-Axis Capabilities
Robotic welding systems with multi-axis capabilities can be a solution for welding complex geometries. These systems utilize multi-axis robots that can manipulate the welding torch in multiple directions, allowing for precise control over the welding process on curved or contoured surfaces. Additionally, using offline programming software, the robot’s movements can be programmed and simulated before the actual welding process, ensuring accurate and consistent welding on complex geometries.
Bonus Solution: Hard Automation Systems with Arc Voltage Control (AVC) Capabilities
Automated welding systems with AVC for GTAW can be a solution for welding complex geometries. These systems utilize Voltage Monitoring that can adjust the arc length of the welding torch within certain selectable parameters. This allows for precise control over the TIG welding process on curved or contoured surfaces that are in longitudinal directions. This can be used on positioners, welding lathes, and seamers.

Weld Control Screen
Welding System Equipment Builders
As experienced designers & builders of automated welding equipment, we thrive on offering practical, effective solutions to welding challenges. Robotic welding can take your manufacturing to the next level with advanced welding automation. Bancroft’s expertise & technology will improve your operations. From simple, stand-alone machines to full robotic welding automation systems. We are a welding equipment builder uniquely qualified to provide reliable, cost-effective solutions to fit your needs. Contact us today to learn more!