Finding the Right Tool for the Job – Welding Automation Types
On the fence about whether welding automation can actually work—AND be profitable—for your business and project applications? We realize how imperative it is to get answers upfront to all your automation questions. We’ve put together this comprehensive guide to help you through the basics.
Automaton Works to:
- Improve weld quality
- Enhance safety and the overall well-being of operators
- Increase productivity
- Attract skilled workers
- Lower ongoing costs
- Grow your bottom line
3 Needs to Move Forward in Automation
1. Workpiece Uniformity
Why is uniformity SO critical?
All automation or semi-automatic welding equipment is programmed on a “master part,” meaning the welding path and framework is set and then repeated over and over. When the part location or welding condition changes, the automated equipment will not know without adjustments made by the operator. Therefore, part uniformity is one of the most important aspects of any automated process. One of the best ways to improve inconsistencies is to address the source!
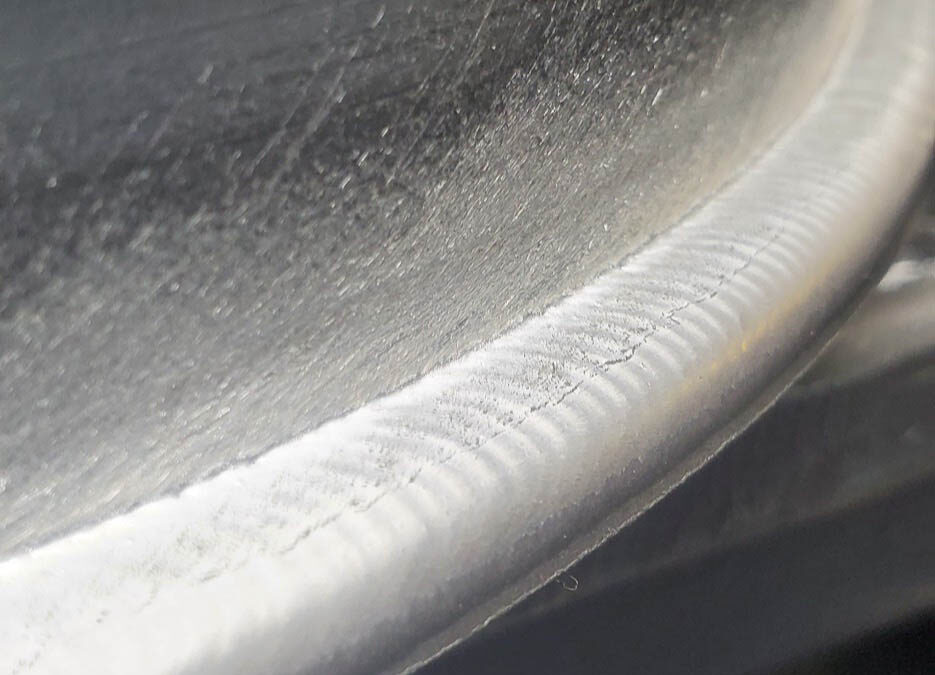
Quality and consistency through repeatability is the most predominant perk to welding automation.
2. Opportunity
If you’re under the impression that you need a complex or large-scale weldment in order to make automation worthwhile, think again. We’ve noticed many shops experience huge gains from automating simple or small parts. This strategy allows for automation to do what it does best on the simplistic parts and gives your skilled welders time to focus on more complicated projects.
3. The Right Team
We talk a lot about teaming up with a reputable welding automation partner or integrator. Along with an experienced team like Bancroft Engineering, the most successful long-term automation gains come from teams of operators who have a high level of ownership and are willing to problem solve to get the job done right.
3 Types of Welding Automation
Having a full understanding of the automated welding solutions available, along with their benefits and drawbacks, is the first step to making the right choice for your needs. Here are the three main types of welding automation:
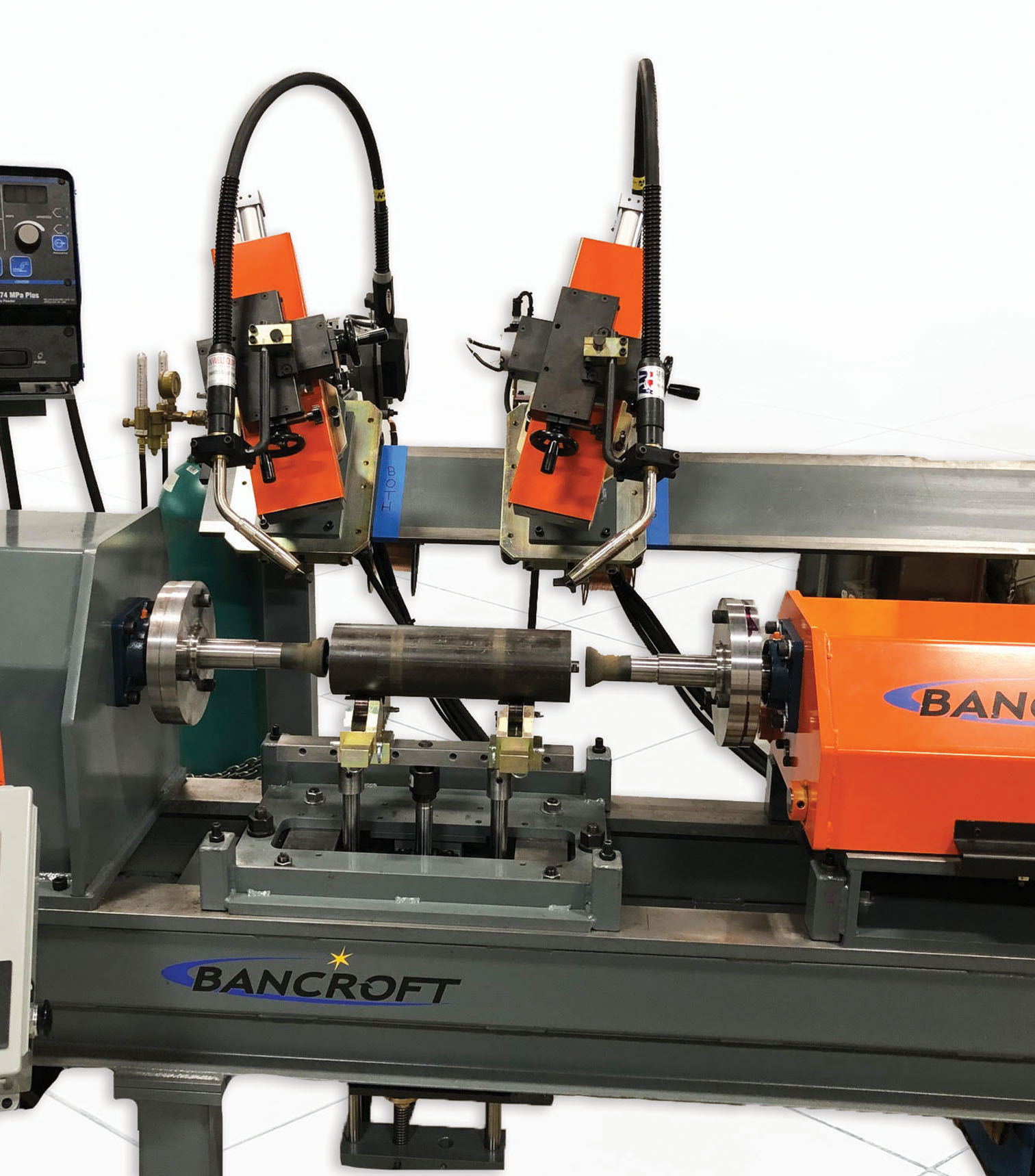

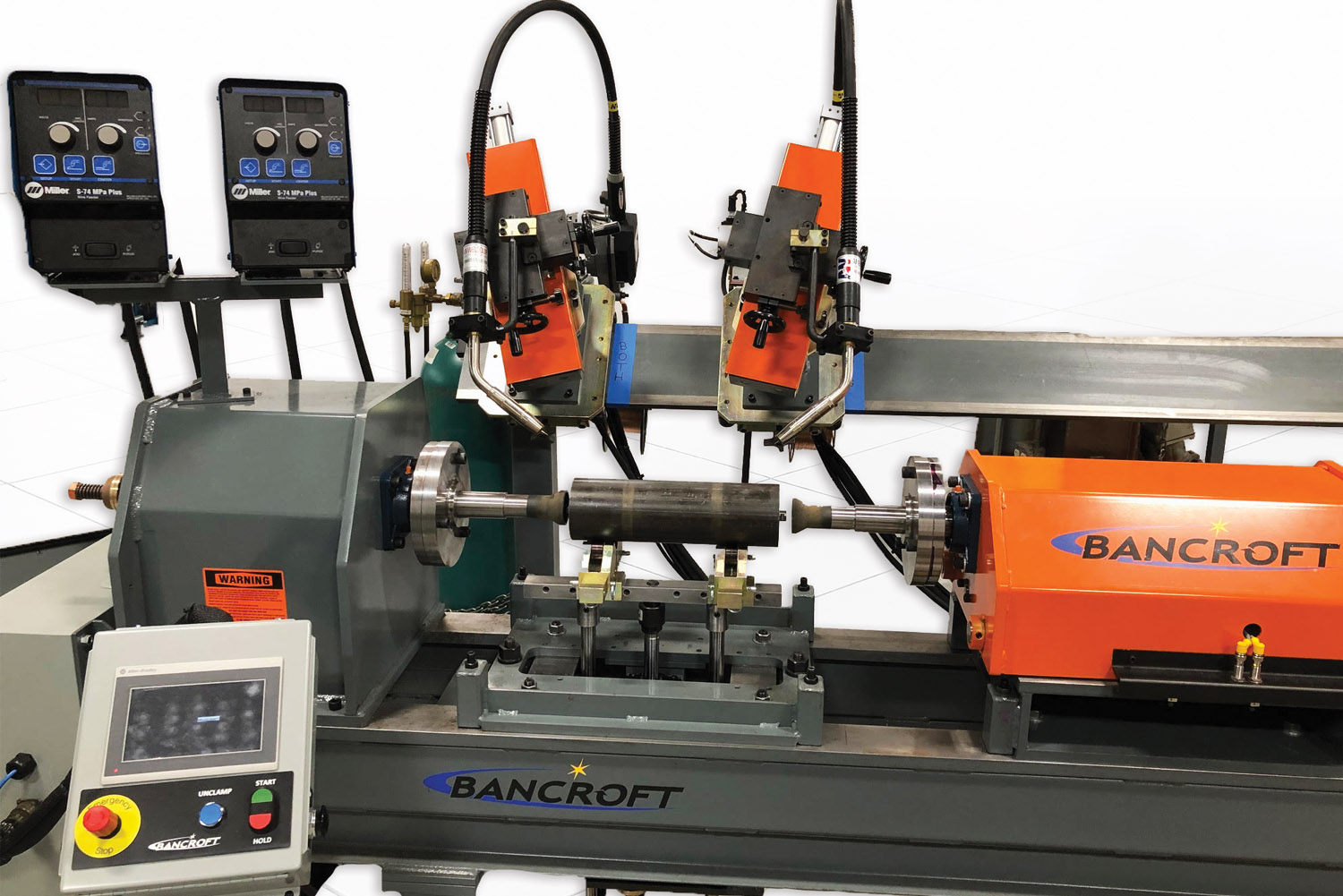
Fixed Automation
Fixed welding automation equipment is built and designed to weld a specific part or part-family. This is one of the most cost-effective forms of automation. A few examples of fixed automation systems include linear welders, rotary welders and circle welders, seam welders and circumferential welders. This solution is best for high volume parts.
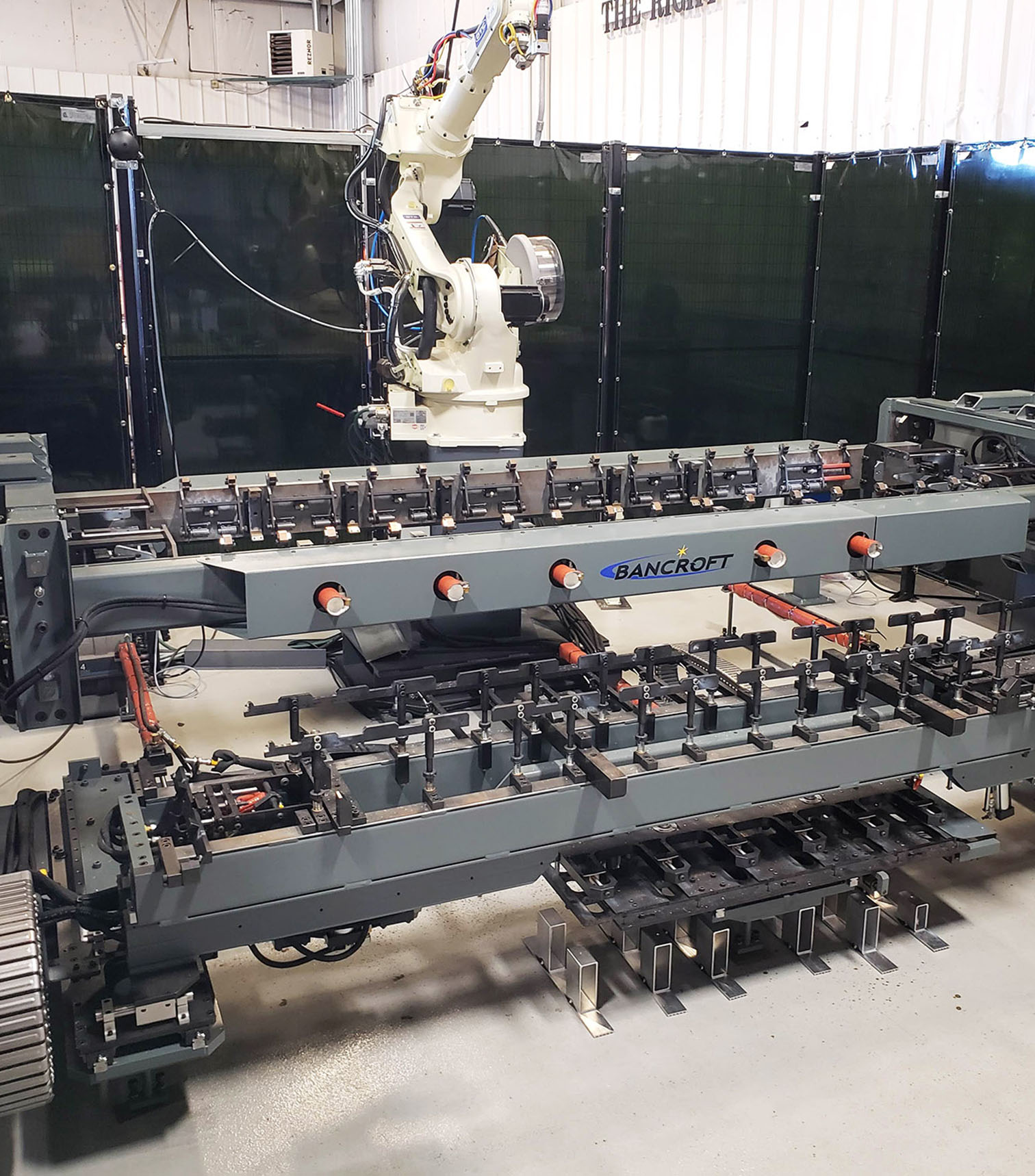
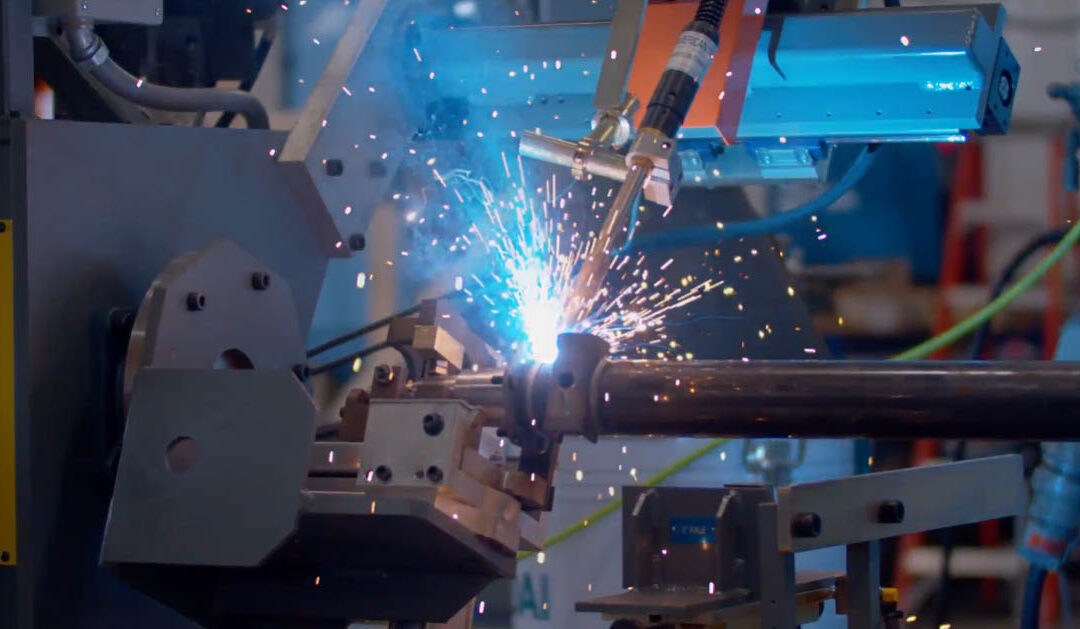
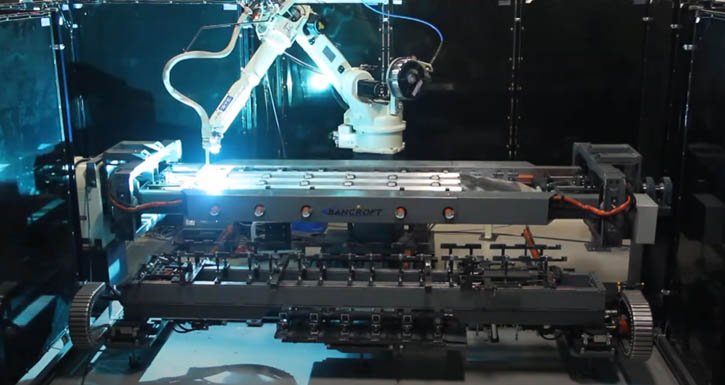
Robotic Welding
Traditional robotic welding is what most think of when it comes to welding automation. Robots come in all sizes and are offered by robot manufacturers, suppliers, and integrators. Robots require a certain set of safety equipment to protect humans such as guarding, fences and sensors. The best fits for robotic welding are large parts, complicated welding, and high-volume operations.
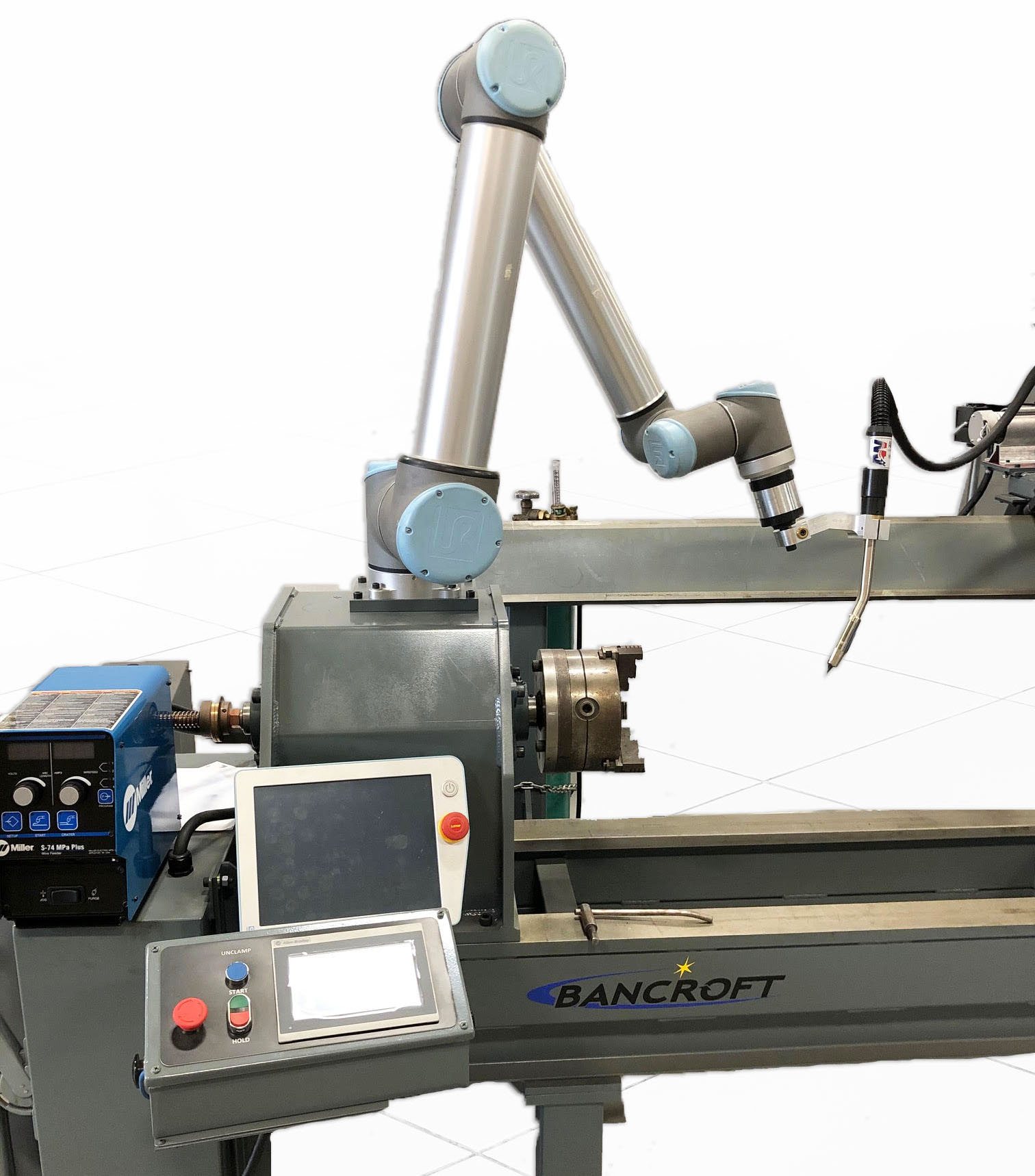

Collaborative Automation
One of the newest forms of automation is collaborative technology. Collaborative robots include internal sensors, allowing humans to work directly with the robot in the same space. This eliminates the need for safety fences and frees up more shop floor space. Collaborative welding automation is best for low volume production and for those needing a lot of flexibility.
With over 50 years of welding equipment experience, Bancroft Engineering has worked to improve automated welding processes for hundreds of businesses. We’re always ready for your specific application questions—get in touch with our engineers today!